Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) in (NZB x NZW)F1 Mice
(also a model of secondary Sjögren's syndrome)
(NZB x NZW)F1 mice (also referred to as NZBWF1 mice) spontaneously develop autoimmune diseases closely resembling SLE and secondary Sjögren's syndrome. We routinely run this model in female NZBWF1 mice.
Similar to human patients with SLE, these mice develop high concentrations of autoimmune anti-dsDNA and anti-nuclear antibodies, proteinuria, and immune complex glomerulonephritis. Production of anti-nuclear and anti-dsDNA antibodies is detectable as early as 20 weeks of age. Mice develop extensive kidney pathology over a range of ages, typically following decline in body condition and several weeks of high proteinuria scores. As in human patients, disease in NZBWF1 mice is polygenic and spontaneous, making this the best model of human SLE, with excellent predictive value for drug efficacy.
These mice also develop inflammation in the submandibular and lacrimal glands closely resembling secondary Sjögren's syndrome.
Treatment usually starts when mice are 21 to 24 weeks old, when initial signs of disease are normally present in some mice, but before severe proteinuria and irreversible kidney damage develop in most mice. By 42 weeks of age, 80 to 100% of untreated mice will develop glomerulonephritis.
Our standard in vivo readouts are proteinuria and body weight. Proteinuria is measured weekly and body weight is measured twice per week.
At the end of the study, we can perform histology on kidneys, submandibular glands, and lacrimal glands. We can also perform flow cytometric analysis on splenocytes and kidney infiltrating cells. We can also measure blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in serum, and measure anti-dsDNA antibodies in serum or plasma.
Please contact Hooke at or with questions or for a quotation.
Typical results - SLE
Mice were treated from week 23 of life (Week 23) through the end of the study (Week 42). Proteinuria was measured once per week and body weight twice per week from Week 21. Serum was collected from all mice at Weeks 23 and 34 for anti-dsDNA IgG antibody measurement, and at Week 42 for anti-dsDNA IgG antibody and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) measurement. Left kidneys were collected for histological analysis from all mice at the end of the study. Right kidneys and spleens were collected from all remaining mice in the Vehicle group and from 7 representative mice in the Cyclophosphamide group for flow cytometric analysis.
All figures show mean + SEM or mean ± SEM, and all tables show mean ± SD.
Clinical readouts
As shown below, cyclophosphamide treatment inhibits disease development as evidenced by significantly lower proteinuria scores at the end of the study. Mice treated with cyclophosphamide typically experience an early spike in proteinuria.
| Treatment | # mice | End proteinuria score | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | 14* | 3.43 ± 0.81 | - |
| Cyclophosphamide | 15 | 1.97 ± 0.23 | <0.001 |
*One (1) mouse was euthanized at Week 35 due to complications of lymphadenopathy and all readouts were therefore excluded after euthanasia.
End proteinuria scores compared using Wilcoxon's non-parametric test.
Tissue weights at termination
| Treatment | Kidney (mg)* | p value | Spleen (mg) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | 225 ± 49 | - | 148 ± 49 | - |
| Cyclophosphamide | 192 ± 19 | 0.022 | 48 ± 6 | <0.001 |
Kidney and spleen weights compared using 2-tailed Student's t-test.
*For each mouse, the average weight of both kidneys was calculated and used for analysis.
BUN and anti-dsDNA measurements
| Treatment | BUN in serum (mg/dL) | p value |
|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | 64.5 ± 47.0 | - |
| Cyclophosphamide | 19.2 ± 3.4 | <0.001 |
BUN in serum concentrations compared using 2-tailed Student's t-test.
| anti-dsDNA IgG (units/mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Week 23 (Baseline) |
Week 34 | p value | Week 42 (Terminal) |
p value |
| Vehicle | 436 ± 458 | 1268 ± 1377 | - | 2189 ± 1517 | - |
| Cyclophosphamide | 194 ± 110 | 0.006 | 191 ± 81 | <0.001 | |
Anti-dsDNA antibody concentrations compared using 2-tailed Student's t-test.
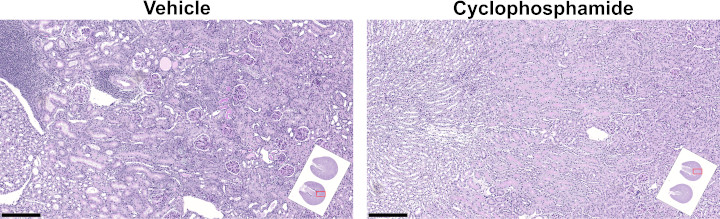
Histological analysis of kidneys at termination
| Histological analysis of kidneys at termination | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Total glomerular lesion | p value | Total tubular and interstitial lesion | p value | Total kidney lesion | p value |
| Vehicle | 4.9 ± 2.7 | - | 1.1 ± 1.0 | - | 6.1 ± 3.6 | - |
| Cyclophosphamide | 0.4 ± 0.9 | <0.001 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | <0.001 | 0.4 ± 0.9 | <0.001 |
Kidney lesion scores compared using Wilcoxon's non-parametric test.
For a higher resolution image, click on the image above. Scale bars are 250 µm. Insets illustrate left kidney transverse sections at the hilus (kidney cut in half, both halves embedded and sectioned), with red outlines indicating the locations of the magnified images.
Flow cytometric analysis of kidneys at termination
| Flow cytometric analysis of kidneys - proportion of cells | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | # mice | CD45+ in live cells (%) | p value | B220+CD4- in CD45+ cells (%) | p value | B220-CD4+ in CD45+ cells (%) | p value |
| Vehicle | 10 | 25.2 ± 12.1 | - | 6.6 ± 3.1 | - | 25.1 ± 9.3 | - |
| Cyclophosphamide | 7 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | <0.001 | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 0.009 | 34.8 ± 6.0 | 0.008 |
Cell population proportions compared using 2-tailed Student's t-test.
| Flow cytometric analysis of kidneys - number of cells | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Total live (x103) | p value | CD45+ (x103) | p value | CD45+B220+ CD4- (x103) |
p value | CD45+B220-CD4+ (x103) | p value |
| Vehicle | 1664 ± 425 | - | 458 ± 313 | - | 24.4 ± 11.6 | - | 104 ± 71 | - |
| Cycloph. | 874 ± 219 | <0.001 | 20 ± 5 | 0.002 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | 7 ± 2 | 0.002 |
Cell numbers compared using 2-tailed Student's t-test.
Flow plots of CD45+ cells
Flow cytometric analysis of spleens
| Flow cytometric analysis of spleens - proportion of cells | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | # mice | CD45+ in live cells (%) | p value | B220+CD4- in CD45+ cells (%) | p value | B220-CD4+ in CD45+ cells (%) | p value |
| Vehicle | 10 | 99.7 ± 0.7 | - | 55.9 ± 6.8 | - | 24.6 ± 2.8 | - |
| Cyclophosphamide | 7 | 98.9 ± 0.5 | 0.733 | 27.6 ± 4.3 | <0.001 | 39.1 ± 12.8 | <0.001 |
Cell population proportions compared using 2-tailed Student's t-test.
| Flow cytometric analysis of spleens - number of cells | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Total live (x106) | p value | CD45+ (x106) | p value | CD45+B220+CD4- (x106) | p value | CD45+B220-CD4+ (x106) | p value |
| Vehicle | 115.5 ± 27.9 | - | 114.4 ± 27.6 | - | 64.9 ± 19.5 | - | 28.0 ± 6.5 | - |
| Cyclophosphamide | 23.4 ± 7.1 | <0.001 | 23.2 ± 7.0 | <0.001 | 6.5 ± 2.6 | <0.001 | 9.0 ± 2.5 | <0.001 |
Cell numbers compared using 2-tailed Student's t-test.
Flow plots of CD45+ cells
Typical results - secondary Sjögren's syndrome
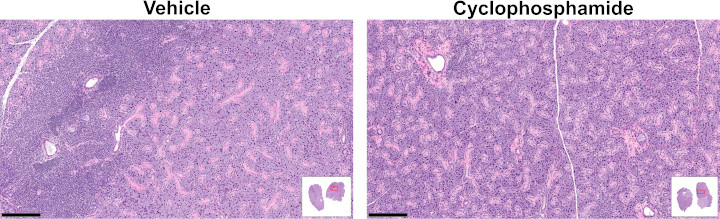
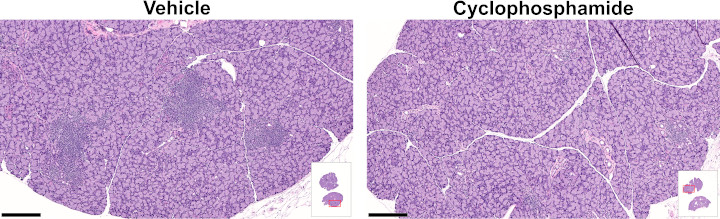
Mice were treated from Week 21 through the end of the study (Week 41). Submandibular and lacrimal glands were collected for histological analysis at the end of the study. Inflammatory foci per section were counted; graphs show mean ± SEM, table shows mean ± SD.
| Submandibular gland | Lacrimal gland | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | # mice | Inflammatory foci per section |
p value | Inflammatory foci per section |
p value |
| Vehicle | 16 | 56.9 ± 19.2 | - | 22.1 ± 8.5 | - |
| Cyclophosphamide | 12 | 7.2 ± 8.5 | <0.001 | 7.6 ± 8.9 | <0.001 |
Numbers of inflammatory foci compared using 2-tailed Student's t-test.
For a higher resolution image, click on the image above. Scale bars are 250 µm. Insets illustrate longitudinal submandibular gland sections (2 glands) with red outlines indicating the locations of the magnified images.
For a higher resolution image, click on the image above. Scale bars are 250 µm. Insets illustrate longitudinal lacrimal gland sections (2 glands) with red outlines indicating the locations of the magnified images.


_150px.jpg)