Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) in DBA/1 Mice
Hooke has extensive experience with CIA, one of the most commonly used animal models of human rheumatoid arthritis. The CIA model is usually run in DBA/1 mice, but the disease can also be induced in B10.R111 mice, B10.Q mice, and Lewis rats.
Please contact Hooke at or with questions or for a quotation.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
RA is an autoimmune disease affecting primarily joints, but also connective tissue in the heart, blood vessels, lungs, eyes, skin, and kidneys. RA affects more women than men (~2:1). Joint inflammation is characterized by pain, swelling and stiffness, development of adhesions, erosion of joint surfaces, bone resorption, loss of function and joint deformation.
Approved treatments for RA include:
- NSAIDs
- Corticosteroids
- Methotrexate
- JAK inhibitors - Olumiant (baricitinib), Rinvoq (upadacitinib), Xeljanz (tofacitinib)
- TNF-blocking - Cimzia (certolizumab pegol), Enbrel (etanercept), Humira (adalimumab), Remicade (infliximab), Simponi (golimumab)
- IL-1 blocking - Ilaris (canakinumab), Kineret (anakinra)
- IL-6 blocking - Actemra (tocilizumab)
- IL-12/IL-23p40 blocking - Stelara (ustekinumab)
- B cell depleting - Rituxan (rituximab)
- CTLA4-Ig - Orencia (abatacept)
CIA model
The joint inflammation which develops in CIA resembles inflammation in human patients with RA. Therapeutics which reduce RA in human patients (such as those listed above) are also efficacious in CIA. Compound efficacy in the mouse CIA model has excellent predictive value for efficacy in RA.
CIA is mediated by both T cells and antibodies (B cells). Macrophages are believed to play an important role in mediating tissue damage during disease development.
Disease induction
CIA is induced by immunization with type II collagen emulsified in Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA), followed by a booster immunization with type II collagen emulsified in either CFA or Incomplete Freund's Adjuvant (IFA). Four to ten days after the booster, inflammation develops in mouse paws.
Treatment can be initiated either at the time of immunization (prophylactic treatment), at the time of the booster immunization (semi-therapeutic treatment), or as each mouse develops disease (therapeutic treatment).
This model is 35 to 45 days long.
CIA induction and development
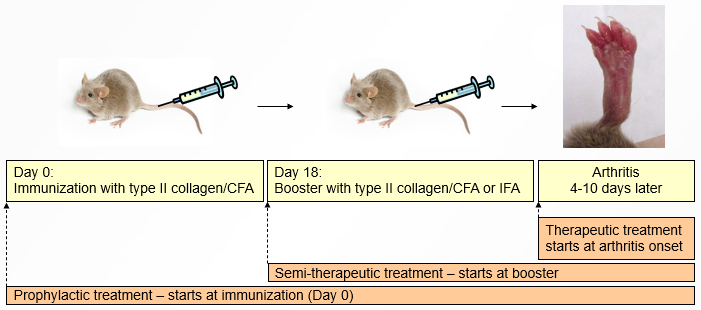
Prophylactic treatment
Treatment starts at immunization and continues for 5 to 6 weeks. Mice are assigned to groups in a balanced manner to achieve similar weight at the time of immunization.
The results below are from a prophylactic CIA study in DBA/1 mice treated with vehicle and positive controls dexamethasone and methotrexate.
Typical results (prophylactic treatment)
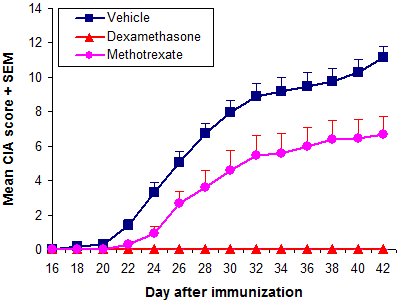
| Treatment | CIA incidence | Median day of onset (all mice) |
p value (onset) |
End score ± SD |
p value (end score) |
End weight (%) ± SD |
p value (end weight) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | 100% | 22.4 ± 0.6 | 11.1 ± 2.6 | 87.4 ± 5.3 | |||
| Dexamethasone | 0.0% | n/a | <0.0001 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | <0.0001 | 84.9 ± 4.8 | 0.2411 |
| Methotrexate | 86.7 | 26.0 | 0.0004 | 6.7 ± 4.2 | 0.0015 | 93.1 ± 6.5 | 0.0128 |
Semi-therapeutic treatment
Semi-therapeutic treatment lies between prophylactic and therapeutic treatment. In this regimen, treatment begins on the day of the booster immunization (some mice may already show initial signs of CIA at that time).Therapeutic treatment
Treatment starts at disease onset, with rolling enrollment as each mouse develops disease. Treatment continues for 14 to 20 days.
Mice are distributed to groups in a balanced manner, to achieve a similar distribution of severity and day of onset in each group. Mice with late onset are excluded. Very consistent groups yield very tight results.
Shown below are typical results from therapeutic CIA studies in DBA/1 mice.
Therapeutic treatment with dexamethasone and methotrexate
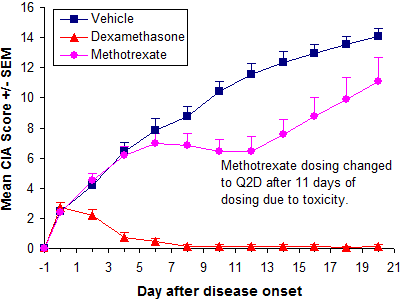
| Treatment | Day of onset ± SD |
Score at onset ± SD |
Score 14 days after onset ± SD |
p value | End score ± SD |
p value | End weight (%) ± SD |
p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | 27.0 ± 1.4 | 2.5 ± 1.2 | 12.3 ± 3.0 | 14.1 ± 2.1 | 90.5 ± 6.0 | |||
| Dexamethasone | 26.9 ± 1.0 | 2.7 ± 1.8 | 0.1 ± 0.5 | <0.0001 | 0.1 ± 0.5 | <0.0001 | 99.0 ± 5.9 | 0.0006 |
| Methotrexate | 27.1 ± 1.0 | 2.4 ± 0.8 | 7.5 ± 3.7 | 0.0021 | 11.1 ± 5.6 | 0.1229 | 91.7 ± 7.9 | 0.6548 |
Therapeutic treatment with anti-TNF and CTLA4-Ig
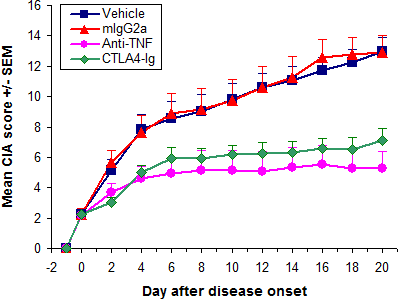
| Treatment | Day of onset ± SD |
Score at onset ± SD |
Maximum score ± SD |
p value | End score ± SD |
p value | End weight (%) ± SD |
p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | 25.5 ± 1.6 | 2.3 ± 1.2 | 13.0 ± 3.0 | 0.7210 | 13.0 ± 3.0 | 0.7206 | 93.8 ± 4.2 | 0.5150 |
| mlgG2a | 25.4 ± 1.4 | 2.3 ± 1.3 | 12.9 ± 3.8 | 12.9 ± 3.8 | 95.1 ± 5.5 | |||
| Anti-TNF | 25.7 ± 1.1 | 2.2 ± 1.1 | 6.2 ± 4.3 | 0.0012 | 5.3 ± 4.0 | 0.0006 | 104.0 ± 3.5 | 0.0001 |
| CTLA4-Ig | 25.7 ± 1.1 | 2.3 ± 1.1 | 7.4 ± 2.5 | 0.0025 | 7.1 ± 2.9 | 0.0022 | 101.1 ± 4.1 | 0.0062 |
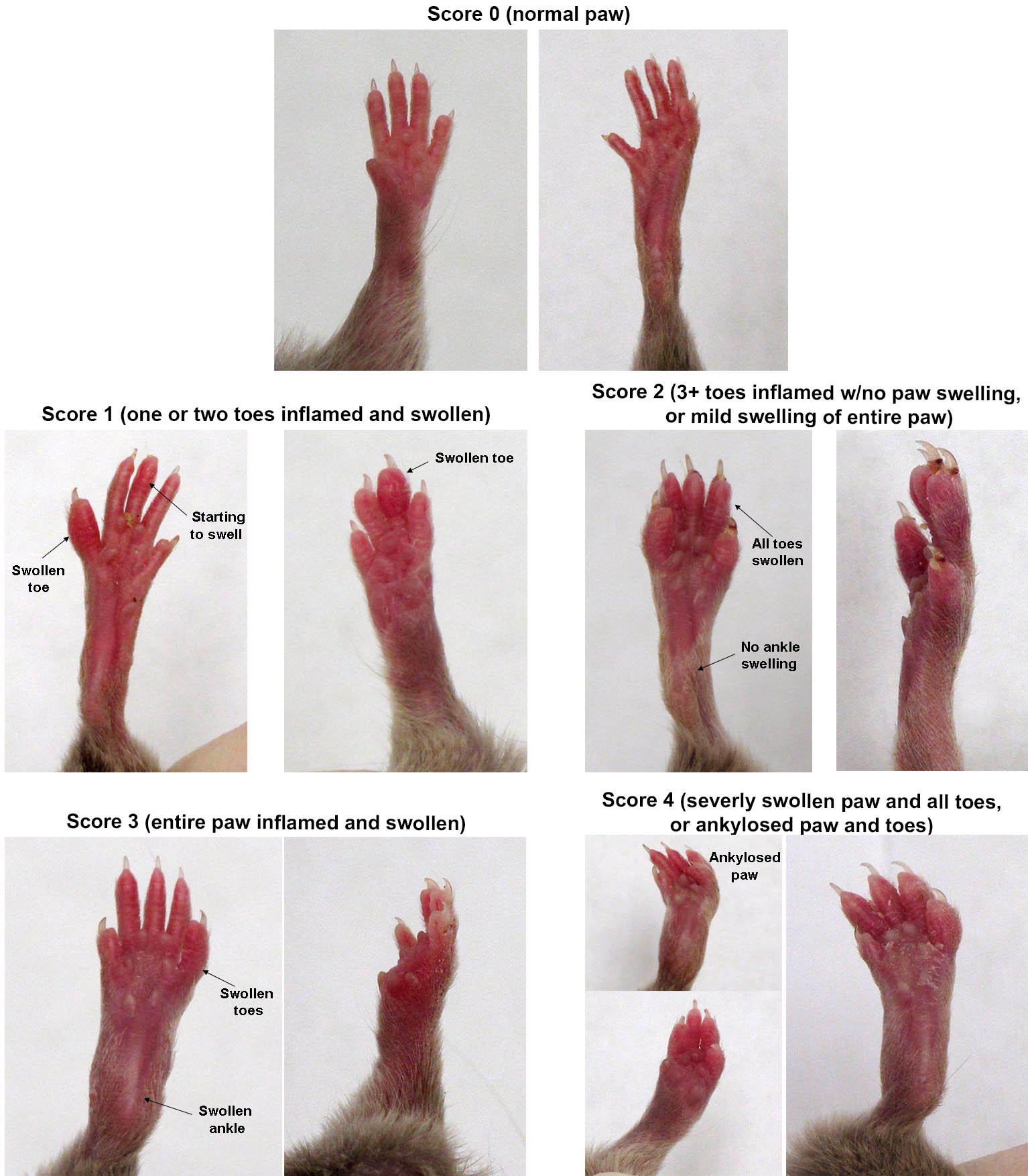
CIA scoring
CIA is scored blind, by a person unaware of both treatment and of previous scores for each animal. Extensive training and practice are critical to repeatable scoring of CIA.
The animal's score is the total of all four paw scores on scale of 0-16, where each paw is scored as follows:
| Paw score | Clinical observations |
|---|---|
| 0 | Normal paw. No obvious differences in appearance vs. healthy mice. |
| 1 | One or two toes inflamed and swollen. No apparent swelling of paw or ankle. |
| 2 | Three or more toes inflamed and swollen, but no paw swelling, OR Mild swelling of entire paw. |
| 3 | Swelling of entire paw and some toes. |
| 4 | Severe swelling of entire paw and all toes, OR Ankylosed paw and toes and the mouse cannot grip the wire top of the cage. |
CIA scoring - typical mouse paw appearance
Histological analysis
Histological analysis is often performed at the end of the study.
Typically, sections are made of ankles, wrists, and paws. Both the number of affected joints and the severity of pathological findings in each section are considered in histological analysis of mice with CIA.
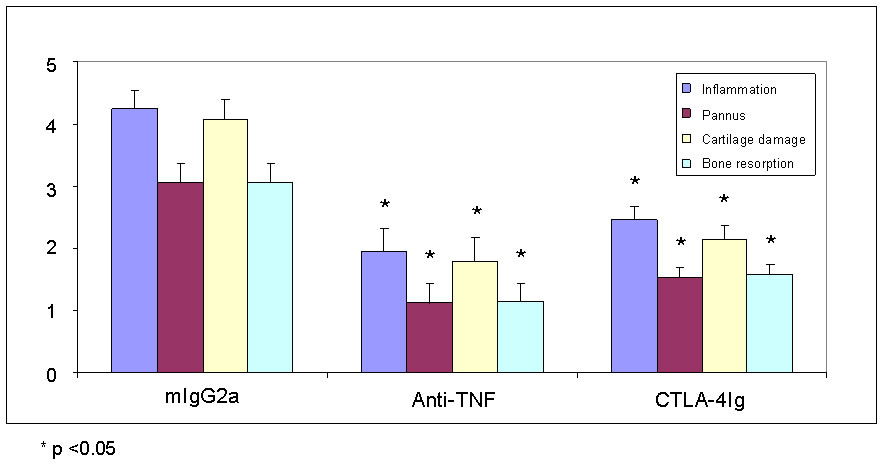
Pathohistological scoring in CIA
Joints are scored for inflammation, cartilage damage, pannus formation, and bone resorption on a scale of 0 to 5 for each readout.
Typical results after therapeutic treatment with mlgG2a, anti-TNF and CTLA4-Ig are shown below.
Representative histological findings - paw sections stained with toluidine blue
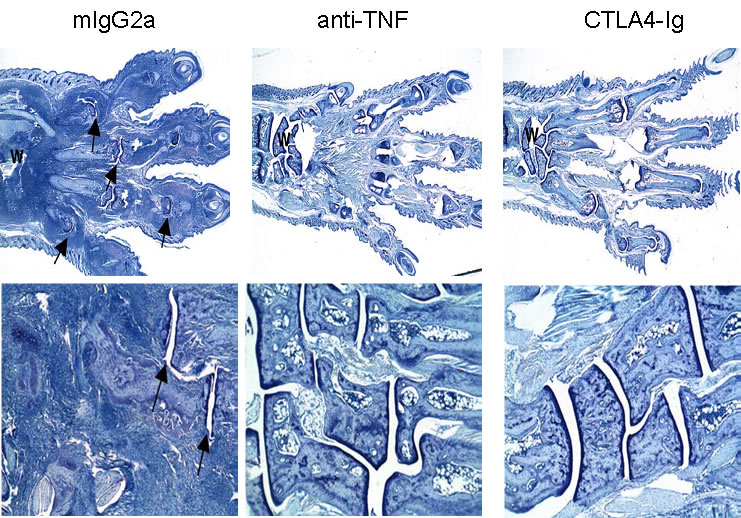
Typical histological results after therapeutic treatment
Results
Interim results are normally reported to the customer weekly, starting after the first clinical signs of CIA are observed. Each includes:
- Raw CIA scores
- Raw body weights
- Graph of average CIA scores for each group over time
- Graph of change in body weight for each group over time
Final results are normally reported within 6 weeks of completing each study and include:
- Raw CIA scores
- Raw body weights
- Statistical analysis and plots (in a spreadsheet):
- Comparison of time to CIA onset
- Comparison of mean maximum CIA scores
- Comparison of CIA scores at the end of the study
- Comparison of change in body weight by the end of the study
- Graph of CIA scores during the study
- Graph of change in body weight from onset until the end of the study
- Prose report, including interpretation of results
Histological analysis (if ordered) is normally reported within 8 weeks of completion of study.
Analyses offered
Some customers order analysis of all groups in advance, but we generally encourage customers to wait for initial results before deciding which analyses to order.
We usually quote a price for your base study, together with prices for additional analysis that may be ordered later. This gives you flexibility to analyze only a sample of animals, choose particular groups for analysis, or even skip analysis completely if the results aren't promising. Our scientists will review your initial results with you, and can recommend the best analyses to maximize return from your study.
We generally ask for 5 day's notice to schedule tissue collection or analysis (but we do our best to accommodate last-minute orders).
The following are the most commonly ordered analyses in CIA studies.
Histological analysis of paws
All four paws of selected mice are collected in 10% buffered formalin at the end of the study. Each paw is prepared and analyzed using one toluidine blue stained section.
Anti-collagen antibodies in serum
Serum is isolated and concentration of anti-collagen antibodies is determined using ELISA.
IL-6 and TNF concentration in serum
IL-6 and TNF concentrations in serum are determined using BD CBA Enhanced Sensitivity Flex Sets kit (BD Biosciences).
Photography of mouse paws
Each paw of selected mice is photographed twice (total of 8 photos/mouse). Original camera image files are sent to the customer without editing or alteration.
Hind paw thickness measurement (therapeutic treatment)
Twice between Days 1 and 14 after immunization (before enrollment begins), both hind paws of all mice are measured using calipers to establish baseline values for paw thickness.
Mice are enrolled into groups when they first show paw swelling. Those mice with a swollen hind paw at that time have the more swollen hind paw measured with calipers. Those mice will thereafter have the same hind paw measured again at each CIA scoring. Mice which were enrolled based on a swollen front paw are not used for readout.
(This readout must be ordered before Day 10 after immunization.)
Short-term assays
Before proceeding with a CIA model study, you may want to run a short-term PK/PD assay as a first-pass screen for drugs aimed at treatment of RA:
See also
- CIA in DBA/1 Mice - Overview and Typical Results (pdf slides)
- CIA Induction in DBA/1 Mice (protocol)


_150px.jpg)