IL-23-Induced Psoriasis in C57BL/6 Mice
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a common chronic inflammatory disease of the skin. It is characterized by increased proliferation and lack of maturation of keratinocytes, which results in thickened skin. The dermis and epidermis are infiltrated with immune cells which, together with keratinocytes, produce proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-23, IL-22, IL-17A, and IL-17F) and keep inflammatory processes in psoriatic lesions active.
Approved treatments for psoriasis include:
- Corticosteroids
- TNF blockers: adalimumab (HUMIRA, Cyltezo); etanercept (Enbrel, Erelzi); infliximab (Remicade)
- IL-17A blockers: ixekizumab (Taltz); brodalumab (Siliq); secukinumab (Cosentyx)
- IL-23 blockers: guselkumab (Tremfya); ustekinumab (Stelara); tildrakizumab (Ilumya)
- PDE4 inhibitor: apremilast (Otezla)
IL-23-induced psoriasis model
IL-23 is a key cytokine in the activation and proliferation of Th17 cells, which play a critical role in psoriasis pathogenesis.
We usually run this model in female C57BL/6 mice. Daily injections of IL-23 in the ear induce cellular infiltration, epidermal thickening analogous to human psoriasis, and induction of cytokines IL-17A and IL-22.
To induce disease, IL-23 is injected intradermally in the ears of mice daily for 4 days (Days 0 through 3), as illustrated below.
Readouts
Our standard in vivo readouts are body weight and ear thickness.
At the end of the study we typically analyze:
- Change in ear thickness
- Ear weight
- IL-17A and IL-22 concentration in ear homogenate
- Ear histology
Please contact Hooke at or with questions or for a quotation.
Typical results
Disease induction was via daily intradermal ear injections of either IL-23 or PBS (negative control for disease; "No rm-IL-23 group").
Treatment was daily with either vehicle (No rm-IL-23 and Vehicle groups) or dexamethasone.
Body weight was measured on Days -3, 0, 2, and 4, and ear thickness was measured on Days 0 and 4. At the end of the study ears were collected, weighed, and cytokines IL-22 and IL-17A measured in ear homogenates.
All graphs below show mean + or ± SEM, and all tables show mean ± SD.
Clinical readouts
| Treatment | # mice | Relative end body weight (% of Day -3) |
p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| No rm-IL-23 | 10 | 102.7 ± 3.0 | - |
| Vehicle | 10 | 104.4 ± 4.2 | 0.511^ |
| Dexamethasone | 10 | 97.9 ± 3.8 | 0.001* |
^ Compared to No rm-IL-23.
* Compared to Vehicle.
Relative end body weights compared using ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. p values for the multiple comparisons test are shown.
| Treatment | Terminal ear thickness (µm) | p value | Change in ear thickness (µm) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No rm-IL-23 | 240 ± 19 | - | 31 ± 19 | - |
| Vehicle | 414 ± 65 | <0.001^ | 203 ± 64 | <0.001^ |
| Dexamethasone | 243 ± 21 | <0.001* | 42 ± 20 | <0.001* |
^ Compared to No rm-IL-23.
* Compared to Vehicle.
Ear thicknesses and changes in ear thickness compared using ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. p values for the multiple comparisons test are shown.
Ear weight
| Treatment | Ear weight (mg) | p value |
|---|---|---|
| No rm-IL-23 | 23.6 ± 2.6 | - |
| Vehicle | 35.3 ± 9.1 | <0.001^ |
| Dexamethasone | 21.6 ± 3.0 | <0.001* |
^ Compared to No rm-IL-23.
* Compared to Vehicle.
Ear weights compared using ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. p values for the multiple comparisons test are shown.
IL-22 and IL-17A concentrations in ear homogenates
| Treatment | Ear homogenate IL-22 (pg/mL) |
p value | Ear homogenate IL-17A (pg/mL) |
p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No rm-IL-23 | 7 ± 1 | - | 6 ± 1 | - |
| Vehicle | 3352 ± 1197 | <0.001^ | 53 ± 24 | <0.001^ |
| Dexamethasone | 94 ± 65 | <0.001* | 6 ± 4 | <0.001* |
^ Compared to No rm-IL-23.
* Compared to Vehicle.
Cytokine concentrations compared using ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. p values for the multiple comparisons test are shown.
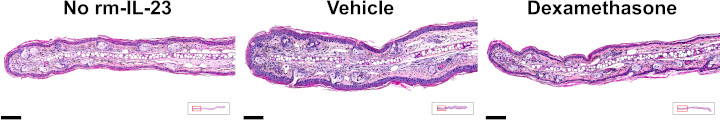
Ear epidermal thickness
At the end of the study ears were collected and processed for histological analysis of epidermal thickness. For each sample epidermal thickness was determined as the area of the epidermis divided by the epidermal length.
The graph shows mean ± SEM, and the table shows mean ± SD.
| Treatment | Average ear epidermal thickness (µm) | p value |
|---|---|---|
| No rm-IL-23 | 41.2 ± 4.6 | - |
| Vehicle | 77.7 ± 8.0 | <0.001^ |
| Dexamethasone | 40.9 ± 4.8 | <0.001* |
^Compared to No rm-IL-23.
*Compared to Vehicle.
Average ear epidermal thicknesses compared using ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. P values for the multiple comparisons test are shown.
For a higher resolution image, click on the image above. Scale bars are 100 µm. Insets illustrate transverse sections of ears, with red outlines indicating the locations of the magnified images.


_150px.jpg)