LPS-Induced Cytokine Production In Vivo
The concentrations of TNF, IL-6, and IL-1 in serum increase after injection of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
This short-term assay is often used as a first-pass screen for drugs aimed at treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), prior to testing in the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model. Suppression of these cytokines has good predictive value for drug efficacy in CIA.
LPS-Induced Cytokine Production In Vivo
.jpg)
Test compounds are administered to female C57BL/6 mice. One (1) hour later, mice receive a single intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) at 100 ng/mouse. In untreated mice, this activates innate immune response cells and cytokine production.
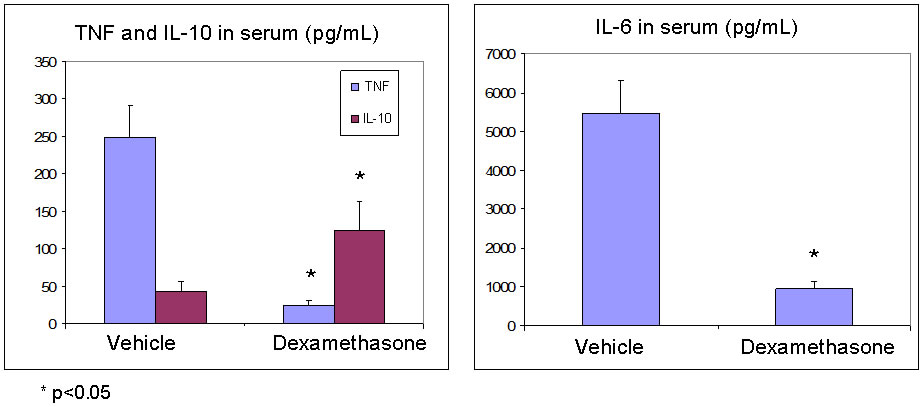
High concentrations of IL-6 and TNF can be detected in serum approximately 2 hours after LPS injection. Both IL-6 and TNF are validated targets for treatment of RA; this assay can evaluate the ability of a compound to suppress production of these cytokines.
Dexamethasone is usually used as a positive control; it greatly reduces serum concentrations of IL-6 and TNF, while increasing serum concentrations of IL-10.
This is a very cost-efficient assay, as it is short (1 day in vivo, 1 day for cytokine analysis) and allows simultaneous testing of both PK and in vivo efficacy using very small compound amounts, since only a single administration of compound is needed.
This model can also be run in other mouse strains.
Please contact Hooke at or with questions or for a quotation.
Typical results
See also
References
[1]
Ghezzi P, Sipe JD, Lymphokine Res. 7:157 (1988)
[2]
Le Contel C, Vinit MA, Parant FJ, Parant MA, Cytokine 2:375 (1990)
[3]
Engelberts I, von Asmuth EJ, van der Linden CJ, Buurman WA, Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 10(1-2):127 (1991)
[4]
Durez P, Abramowicz D, Gerard C, Van Mechelen M, Amraoui Z, Dubois C, Leo O, Velu T, Goldman M, J Exp Med. 177:551 (1993)
[5]
Pengal RA, Ganesan LP, Wei G, Fang H, Ostrowski MC, Tridandapani S, Mol Immunol. 43:1557 (2006)


_150px.jpg)